Disclaimer:
The authors are solely responsible for the content of this report. Material included herein does not represent the opinion of the European Community, and the European Community is not responsible for any use that might be made of it.
Back to overview reports
Eight high scoring conflicts were recorded. These centre around:
As noted earlier in text, interaction areas are frequently aligned with conservation protection - flood protection - ports and navigation requirements, with the specific synergisms resulting from flood protection services also notable in addition to those that occur within a topic area.
As such, the identification of these relatively generic high scoring interactions (both negative and positive) are of value in terms of establishing a typology of management needs, this in turn providing a basis for the translation of management requirements into an Ecosystem Service common currency, and thus linking this to the provision of mitigation and compensation measures. However, whilst these high level typologies provide an indication of the main interaction areas, it is important to emphasise that estuary specific interactions will require specific management focus as discussed in detail in earlier sections of this report. This focus necessarily will have both estuary and topic specific components, although again, the application of these, using appropriate mitigation/compensation measures can be assessed using an Ecosystem Services approach .
Table 9: Strong negative and positive associations between uses/users for all TIDE estuaries combined.
Back to top
How can multiple estuarine resource use be managed in an integrated way within the existing planning system?
How can the Ecosystem Services Approach be used to support management decisions?
How do TIDE estuaries deal with management problems?
How does the societal demand for ecosystem services vary along the estuary gradient?
What are the key areas of conflicts or synergies in TIDE estuaries?
What tool is available to help manage multiple users of a resource in an integrated way (i.e. achieving more holistic management)?
What tools are useful for involving local communities and stakeholders?
Which aspects do I have to take into account in order to make a measure a success?
Which synergistic effects and conflicts can be expected by planning and implementing a certain measure?
Analysis of the TIDE Estuarine Conflict Matrices
Table of content
- 1. SUMMARY
- 2. INTRODUCTION
- 2a. General
- 2b. Research Aims
- 2c. Conflict Matrices
- 2d. Conflict Matrix Tool
- 3. CONFLICT MATRIX METHODOLOGY
- 3a. Approach
- 3b. Analysis
- 4. CONFLICT MATRIX SET-UP PROCESS FINDINGS
- 4a. Salinity/Management Zone Extent Comparison
- 4b. Regional Working Group (RWG) Composition and Interests Comparison
- 4c. Conflict Matrix Estuary Zone Level of Use Comparison
- 4d. Generic Estuary Conflict Scores
- 5. CONFLICT MATRIX OUTCOMES ANALYSIS PER ESTUARY & ZONE
- 5a. Elbe Estuary Conflicts Analysis
- 5b. Weser Estuary Conflicts Analysis
- 5c. Scheldt Estuary Conflicts Analysis
- 5d. Humber Estuary Conflicts Analysis
- 5e. Estuary Conflict Matrix Analysis Summary
- 6. TYPOLOGY OF ASSOCIATIONS ACROSS ALL TIDE ESTUARIES
- 6a. Management Awareness and Focus
- 6b. Salinity Zone Associations
- 6c. Conflict Interaction Typology
- 7. DISCUSSION & RECOMMENDATIONS
- 7a. Spatial Conflict Variation
- 7b. Sectoral Conflict Variation
- 7c. Conflict Management
- 7d. Measures Interactions and Disbenefits
- 7e. Links to Other Approaches
- 8. REFERENCES
- 9. APPENDICES
6c. Conflict Interaction Typology
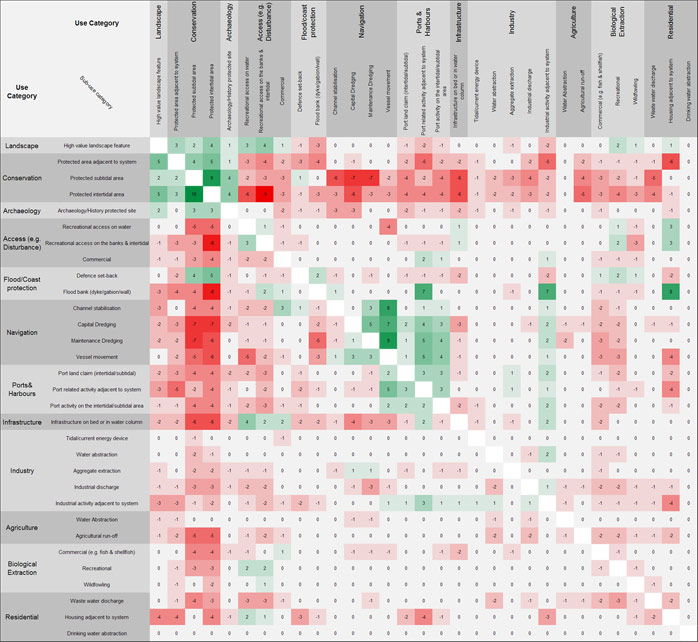
The analysis has identified a series of user interactions that are present across most zones in the TIDE estuaries, and these are shown as a mean score across all zones and all estuaries in Figure 27 and Table 9. Table 9 therefore summarises the main interactions observed from the conflict matrix process across the TIDE estuaries, both antagonistic and synergistic.Eight high scoring conflicts were recorded. These centre around:
- Conservation on Navigation;
- Conservation on Access;
- Access on Conservation;
- Flood Protection on Conservation;
- Navigation on Conservation.
- Conservation on the intertidal zone is impacted by:
- Recreational access along the banks & intertidal zone;
- Provision of flood bank protection;
- Capital dredging for navigation.
- Conservation on the subtidal zone is impacted by:
- Capital dredging for navigation;
- Maintenance dredging for navigation.
- Capital dredging for navigation impacted by:
- Conservation of the subtidal zone.
- Maintenance dredging for navigation impacted by:
- Conservation of the subtidal zone.
- Recreational access along banks and the intertidal zone impacted by:
- Conservation on the intertidal zone
As noted earlier in text, interaction areas are frequently aligned with conservation protection - flood protection - ports and navigation requirements, with the specific synergisms resulting from flood protection services also notable in addition to those that occur within a topic area.
As such, the identification of these relatively generic high scoring interactions (both negative and positive) are of value in terms of establishing a typology of management needs, this in turn providing a basis for the translation of management requirements into an Ecosystem Service common currency, and thus linking this to the provision of mitigation and compensation measures. However, whilst these high level typologies provide an indication of the main interaction areas, it is important to emphasise that estuary specific interactions will require specific management focus as discussed in detail in earlier sections of this report. This focus necessarily will have both estuary and topic specific components, although again, the application of these, using appropriate mitigation/compensation measures can be assessed using an Ecosystem Services approach .
Table 9: Strong negative and positive associations between uses/users for all TIDE estuaries combined.
| Impact of | Impact On | Score | ||
| Category | Activity | Category | Activity | |
| Conservation | Protected subtidal area | Navigation | Capital dredging | -7 |
| Conservation | Protected subtidal area | Navigation | Maintenance dredging | -7 |
| Conservation | Protected intertidal area | Access (e.g. disturbance) | Recreational access on the banks & intertidal | -9 |
| Access (e.g. disturbance) | Recreational access on the banks & intertidal | Conservation | Protected intertidal area | -8 |
| Flood/Coast protection | Flood bank (dyke/gabion/wall) | Conservation | Protected intertidal area | -8 |
| Navigation | Capital dredging | Conservation | Protected subtidal area | -7 |
| Navigation | Capital dredging | Conservation | Protected intertidal area | -7 |
| Navigation | Maintenance dredging | Conservation | Protected subtidal area | -7 |
| Conservation | Protected subtidal area | Conservation | Protected intertidal area | 9 |
| Conservation | Protected intertidal area | Conservation | Protected subtidal area | 10 |
| Flood/coast protection | Flood bank (dyke/gabion/wall) | Ports & Harbours | Port related activity adjacent to system | 7 |
| Flood/coast protection | Flood bank (dyke/gabion/wall) | Industry | Industrial activity adjacent to system | 7 |
| Flood/coast protection | Flood bank (dyke/gabion/wall) | Residential | Housing adjacent to system | 8 |
| Navigation | Channel stabilisation | Navigation | Vessel movement | 8 |
| Navigation | Capital dredging | Navigation | Vessel movement | 7 |
| Navigation | Maintenance dredging | Navigation | Vessel movement | 9 |
Important to know
Reports / Measures / Tools
| Report: | Zonation of the TIDE estuaries (Functioning) |
|---|---|
| Report: | Ecosystem Service Assessment of TIDE Estuaries (Functioning) |
| Report: | Legislative Drivers & Sectoral Plan Review of TIDE Estuaries (Governance) |
Management issues
How can management actions be prioritised based on conflict assessment outcomes?How can multiple estuarine resource use be managed in an integrated way within the existing planning system?
How can the Ecosystem Services Approach be used to support management decisions?
How do TIDE estuaries deal with management problems?
How does the societal demand for ecosystem services vary along the estuary gradient?
What are the key areas of conflicts or synergies in TIDE estuaries?
What tool is available to help manage multiple users of a resource in an integrated way (i.e. achieving more holistic management)?
What tools are useful for involving local communities and stakeholders?
Which aspects do I have to take into account in order to make a measure a success?
Which synergistic effects and conflicts can be expected by planning and implementing a certain measure?