Disclaimer:
The authors are solely responsible for the content of this report. Material included herein does not represent the opinion of the European Community, and the European Community is not responsible for any use that might be made of it.
Back to overview measures
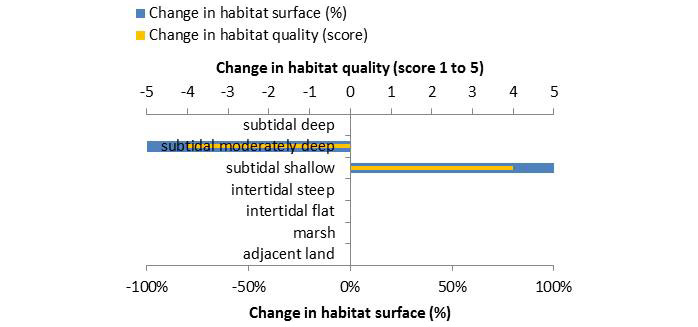
According to expert judgment, we do not have the possibility to indicate the relative involvement of different habitats in percentages and even less to indicate the quality. The reason for this is the fact that the in situ relocation test is just a small scale test to study the feasibility of the large scale relocation along a sandbar, and as such not a goal in itself.
Based on Figure 6, we can however qualitatively conclude that a small area of subtidal shallow habitat was created in front of the sandbar tip. Before the relocation this area was subtidal moderately deep habitat. This is also in line with the objective (creating low dynamic habitat).
Step 2: Expected impact on ecosystem services, compared with targeted ecosystem services, and expected impact on beneficiaries
More information about the methodology and the correct interpretation of the results could be found in the overall measures report (Saathoff et al. 2013).
(1) Overall expected impact on ES:
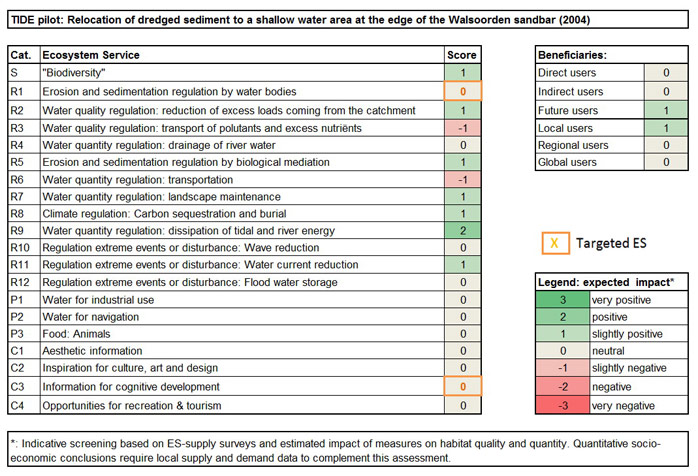
From the ES assessment it is concluded that this measure generates both positive and negative expected impacts. A positive expected impact is indicated for the ES water quantity regulation (dissipation of tidal and river energy). A slightly positive expected impact is indicated for “biodiversity”, and some regulating services (Water quality regulation: reduction of excess loads coming from the catchment; Erosion and sedimentation regulation by biological mediation; Water quantity regulation: landscape maintenance; Climate regulation: carbon sequestration and burial; Regulation of extreme events: water current regulation). A slightly negative expected impact is indicated for the ES Water quality regulation: transport of pollutants and excess nutrients, and Water quantity regulation: transportation.
(2) Expected impact on targeted ES
As this measure was only a test case, the target was limited to studying the stability of the relocated material (ES ‘Information for cognitive development’ and ‘Erosion and sedimentation regulation by water bodies’). The expected impact on both development targets is nihil (neutral).
(3) Expected impact on beneficiaries
The expected impact for the different beneficiary groups is slightly positive for future use and local use.
Back to top
Walsoorden pilot part A (2004): relocation of dredged sediment to a shallow water area at the edge of the Walsoorden sandbar
Table of content
- 1. Description of measure
- 1a. Measure description
- 1b. Monitoring
- 1c. Monitoring results
- 2. Execution of main effectiveness criteria
- 2a. Effectiveness according to development targets of measure
- 2b. Impact on ecosystem services
- 2c. Degree of synergistic effects and conflicts according to uses
- 3. Additional evaluation criteria in view of EU environmental law
- 3a. Degree of synergistic effects and conflicts according to WFD aims
- 3b. Degree of synergistic effects and conflicts according to Natura 2000 aims
- 4. Crux of the matter
- 5. References
Additional information
for this measure:
No further information available.
for this measure:
No further information available.
Impact on ecosystem services
Step 1: Involved habitatsAccording to expert judgment, we do not have the possibility to indicate the relative involvement of different habitats in percentages and even less to indicate the quality. The reason for this is the fact that the in situ relocation test is just a small scale test to study the feasibility of the large scale relocation along a sandbar, and as such not a goal in itself.
Based on Figure 6, we can however qualitatively conclude that a small area of subtidal shallow habitat was created in front of the sandbar tip. Before the relocation this area was subtidal moderately deep habitat. This is also in line with the objective (creating low dynamic habitat).
Step 2: Expected impact on ecosystem services, compared with targeted ecosystem services, and expected impact on beneficiaries
More information about the methodology and the correct interpretation of the results could be found in the overall measures report (Saathoff et al. 2013).
(1) Overall expected impact on ES:
From the ES assessment it is concluded that this measure generates both positive and negative expected impacts. A positive expected impact is indicated for the ES water quantity regulation (dissipation of tidal and river energy). A slightly positive expected impact is indicated for “biodiversity”, and some regulating services (Water quality regulation: reduction of excess loads coming from the catchment; Erosion and sedimentation regulation by biological mediation; Water quantity regulation: landscape maintenance; Climate regulation: carbon sequestration and burial; Regulation of extreme events: water current regulation). A slightly negative expected impact is indicated for the ES Water quality regulation: transport of pollutants and excess nutrients, and Water quantity regulation: transportation.
(2) Expected impact on targeted ES
As this measure was only a test case, the target was limited to studying the stability of the relocated material (ES ‘Information for cognitive development’ and ‘Erosion and sedimentation regulation by water bodies’). The expected impact on both development targets is nihil (neutral).
(3) Expected impact on beneficiaries
The expected impact for the different beneficiary groups is slightly positive for future use and local use.